String Creation:
- Strings can be created by enclosing characters in either single quotes ('') or double quotes ("").
- You can use either single quotes or double quotes consistently within a string, but they cannot be mixed
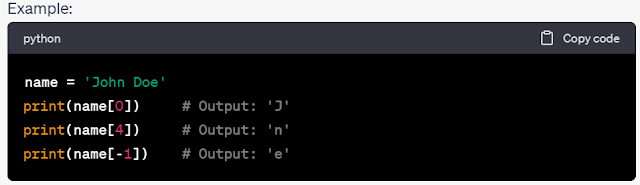
Accessing Characters in a String:
- Individual characters within a string can be accessed using indexing.
- Python uses 0-based indexing, where the first character has an index of 0.
- Negative indexing can be used to access characters from the end of the string.
String Operations:
- Concatenation: Strings can be concatenated using the '+' operator to create a new string that combines multiple strings.
- Repetition: Strings can be repeated using the '*' operator to create a new string with repeated content.
- Length: The 'len()' function returns the number of characters in a string.
String Methods:
- Python provides various built-in methods to manipulate strings. Some commonly used string methods include:
- 'lower()', 'upper()': Convert the string to lowercase or uppercase.
- 'strip()', 'lstrip()', 'rstrip()': Remove leading and trailing whitespace.
- 'split()': Split the string into a list of substrings based on a delimiter.
- 'join()': Join a list of strings into a single string using a delimiter.
- 'replace()': Replace occurrences of a substring with another substring.
- 'find()', 'index()': Find the index of a substring within a string.



Comments
Post a Comment